From Burns to Broken Bones: First Aid Guide for 9 Emergencies
Emergencies can happen anytime and anywhere and being prepared with the knowledge and skills to provide first aid can mean the difference between life and death. In this blog post, we will discuss first aid for 9 of the most common emergencies. From heart attack to choking and poisoning, we will cover the do's and don'ts of each emergency.
1. Heart Attack
Blockage of blood flow to the heart causes heart attack and leads to damaging the heart muscle.
Causes of Heart Attack:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Lack of physical activity
- Coronary artery disease
Symptoms Heart Attack:
- Cold sweat
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Pain, pressure, squeezing or fullness in chest
- Pain or uneasiness in the arms, neck, jaw or stomach
Steps to provide first aid for heart attack:
Do's:
- 1) Call for emergency medical help immediately.
- 2) Encourage the person to sit down and stay calm.
- 3) Give them aspirin if they are not allergic and have no medical contraindications.
Don'ts:
- Don't let the person lie down flat or do any physical activity
- Don't let the person eat or drink.
Causes of Stroke:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Atrial fibrillation
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Family history of stroke
Symptoms of Stroke:
- abrupt dizziness or loss of balance
- abrupt severe headache with no known cause
- abrupt confusion or trouble speaking or understanding speech
- abrupt numbness or weakness in the face, arm or leg (especially on one side of the body)
Steps to provide first aid treatment for Stroke:
Do's:
- Note the time the stroke started.
- Call for emergency medical help immediately.
- Help the person lie down flat and turn their head to one side if they are unconscious.
Don'ts:
- Don't let the person eat or drink.
- Don't try to move the person unless they are in danger.
- Don't give any medication without the advice of medical professionals.
3. Seizures (Fits)
Seizures occur when there is abnormal electrical activity in the brain, leading to temporary changes in movement, behavior and consciousness.
Causes of Seizures:
- Infection
- Epilepsy
- High fever
- Brain injury
- Brain tumor
- Irregular amount of sodium or glucose in the blood
Symptoms of Seizures:
- Staring spells
- Loss of consciousness
- Confusion or disorientation
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
- Uncontrolled shaking or convulsions
- Lip smacking or chewing movements
Steps to provide first aid for Seizures:
Do's:
- Remove any tight clothing around the person's neck.
- Clear the area around the person of any sharp or dangerous objects.
- Help the person lie down on their side and cushion their head with something soft.
Don'ts:
- Don't put anything in the person's mouth.
- Don't hold the person down or stop the fits.
- Don't try to give the person any food or drink until they are fully conscious.
4. Choking
Blockage of airway prevents air from entering the lungs and causes choking.
Causes of Choking:
- Eating too quickly
- Not chewing food properly
- Swallowing large pieces of food
- Drinking alcohol before or during a meal
- Medical conditions that affect swallowing
Symptoms of Choking:
- Gasping or wheezing
- Loss of consciousness
- Hands clutching the throat
- Inability to speak or breathe
- Turning blue or gray in the face
Steps to provide first aid for Choking:
Do's:
- Motivate the person to cough if possible.
- Call for emergency medical help if the person is still choking.
- If the person can't cough, stand behind them and perform the Heimlich maneuver (abdominal thrusts).
Don'ts:
- Don't give the person water or other fluids.
- Don't hit the person's back as this can make things worse.
- Don't try to remove the object with your fingers unless you can see it.
5. Bleeding
Bleeding can occur due to injuries, accidents or medical conditions.
Causes of Bleeding:
- Surgery
- Head injuries
- Broken bones
- Internal injuries
- Blood clotting disorders
- Cuts or puncture wounds
Symptoms of Bleeding:
- Pale skin
- Weakness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Bleeding from the wound
- Blood pooling under the skin
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
Steps to provide first aid for Bleeding:
Do's:
- Use clean cloth to apply pressure to the wound.
- If the bleeding doesn't stop, call for emergency medical help.
- Raise the wounded area above the heart to minimize blood flow.
Don'ts:
- Don't remove any objects that are inserted in the wound.
- Don't ignore bleeding that persists for an extended period or is heavy.
- Don't apply heat to the wound as this can increase blood flow and make bleeding worse.
- Don't apply pressure to an actively bleeding wound unless directed by a medical professional.
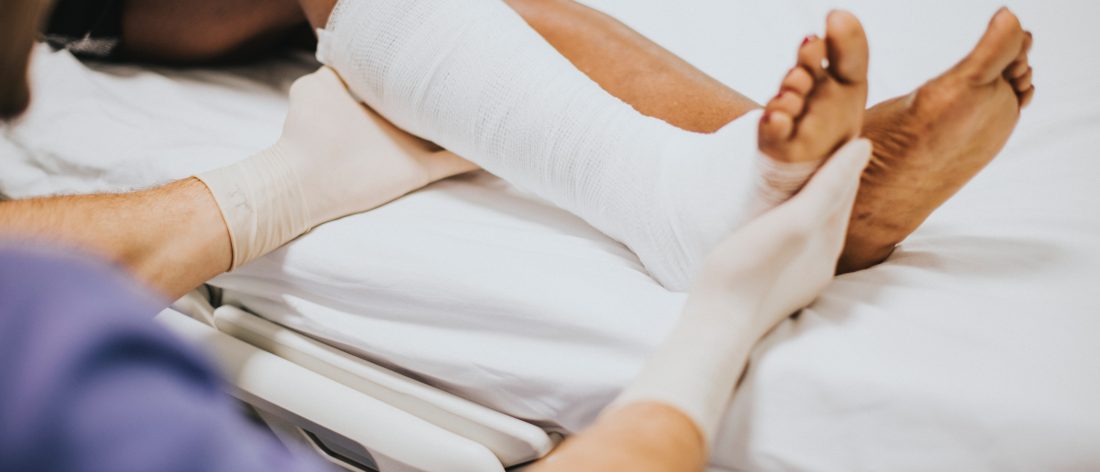
6. Burns:
Causes of Burns:
- Exposure to fire or flames
- Exposure to chemicals or electricity
- Contact with boiling liquids or steam
- Contact with hot objects or surfaces
Symptoms of Burns:
- Redish, swollen skin and pain at the affected area
- Charred or blackened skin
- Blistering or peeling of the skin
- Difficulty in breathing or shortness of breath (if the burn is from inhaling smoke or fumes)
Steps to provide first aid for Burns:
Dos:
- Use cool water to cool down the burns (for at least 10-15 minutes.)
- Cover the burns with an antiseptic, non-stick dressing.
- Take over-the-counter pain medication if necessary.
- Seek medical attention if the burn is severe or if there is any doubt about the severity.
Don'ts:
- Do not try to break blisters
- Do not apply ice or ice water on the affected area.
- Do not apply butter, oil, or other home remedies to the burns.
7. Fracture:
Causes of Fracture:
- Falls
- Medical issues in bones
- Direct blows to the bone
- Repetitive stress or overuse
Symptoms of Fracture:
- Swelling and bruising
- Pain at the site of the fracture
- Deformity or angulation of the affected limb
- Inability to bear weight or use the affected limb
Steps to provide first aid for Fracture:
Dos:
- Immobilize the affected limb with a splint or brace.
- Elevate the affected limb to reduce swelling.
- Take over-the-counter pain medication if necessary.
- Seek medical attention to confirm the fracture and determine the appropriate treatment.
Don'ts:
- Do not apply heat or massage to the affected area.
- Do not attempt to straighten a broken bone or realign a joint.
- Do not attempt to walk or use the affected limb if it is painful.
8. Poisoning:
Causes of Poisoning:
- Bites/stings from poisonous animals/insects
- Exposure to toxic chemicals, such as carbon monoxide or lead
- Ingesting harmful substances, such as drugs, household cleaners, or toxic plants
Symptoms of Poisoning:
- Diarrhea
- Breathing difficulty
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness or confusion
- Seizures or convulsions
Steps to provide first aid for Poisoning:
Dos:
- Remove any remaining poison from the person's mouth or skin.
- Call the poison control center or emergency services immediately.
- Provide any information about the poison that is available.
- If directed by a medical professional, administer first aid, such as inducing vomiting or performing CPR.
Don'ts:
- Do not cause forceful vomiting
- Do not attempt to treat the person without prior knowledge
- Don't let the person eat or drink without consulting a medical professional
9. Electric Shock:
Causes of Electric Shock:
- Lightning strikes
- Contact with exposed electrical wiring or electrical appliances
- Contact with electrically charged objects, such as power lines
Symptoms of Electric Shock:
- Breathing difficulty
- Irregular heartbeat
- Loss of consciousness
- Burns or damage to the skin
- Muscle spasms or contractions
Steps to provide first aid for Electric Shock:
Dos:
- Turn off the switch, if possible.
- Call emergency services immediately.
- Check the breathing and pulse, perform CPR (if required).
- If the person is conscious, keep them calm until medical professionals arrive.
Don'ts:
- Do not touch the person directly if he is in contact with the source of electricity.
- Do not attempt to remove any electrical wires or objects from the person without first turning off the source of electricity.
- Do not attempt to move the person if there is a risk of spinal injury.
Taking care of your health is like putting money in the bank for a rainy day. Understanding the causes and symptoms of common emergencies can help you recognize them early and respond quickly. Remember, if you or someone else is experiencing any of these symptoms, call emergency services right away. Acting fast can make a significant difference in the outcome of an emergency.