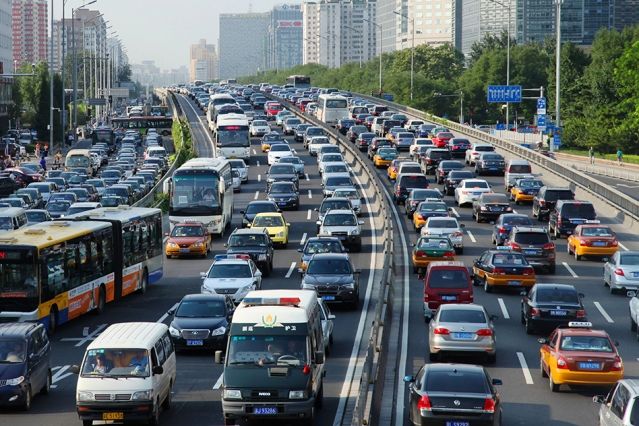
India is a country known for its diverse culture, rich history and vibrant traditions. However, it is also grappling with a grim reality - an alarmingly high rate of road accidents. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), India accounts for more than 150,000 deaths due to road accidents each year, making it one of the leading countries in road accident fatalities. In this blog, we will delve into the causes behind road accidents in India and explore effective safety measures to make our roads safer.
Common Causes of Road Accidents in India
Poor Road Infrastructure: One of the primary contributors to road accidents is the lack of well-maintained roads. Many areas have potholes, uneven surfaces and inadequate road markings, leading to potential hazards for drivers and pedestrians alike.
Reckless Driving: Indian roads are often marred by drivers who exhibit reckless behavior, including overspeeding, aggressive driving, lane-cutting and jumping traffic signals. This reckless driving attitude significantly increases the risk of accidents.
Distracted Driving: With the advent of smartphones and increasing use of electronic devices, distracted driving has become a major issue. Drivers often take their eyes off the road to attend to calls, texts or social media notifications, leading to deadly consequences.
Drunk Driving: Despite stringent laws, driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs remains a prevalent cause of accidents. Impaired judgment and delayed reflexes put not only the driver at risk but also other road users.
Poor Vehicle Maintenance: Many vehicles on Indian roads are poorly maintained, with faulty brakes, worn-out tires and malfunctioning lights. These mechanical issues can be fatal when they lead to accidents on busy roads.
Overloaded Vehicles: Overloading of commercial vehicles, such as trucks and buses, is common in India. This practice compromises the vehicle's stability and maneuverability, increasing the chances of accidents.
Lack of Road Safety Awareness: A significant number of road users, especially in rural areas, lack proper road safety awareness. This ignorance often results in poor decision-making and improper road usage.
Pedestrian Negligence: Pedestrians also play a significant role in road accidents. Jaywalking, crossing roads without using designated pedestrian crossings and disregarding traffic signals contribute to accident rates.
Methods to Prevent Road Accidents
Road Safety Education: Implementing comprehensive road safety education programs is crucial to instill a sense of responsibility and awareness among all road users. This should start from schools and continue through adulthood, emphasizing safe driving practices and pedestrian awareness.
Strict Law Enforcement: Effective enforcement of traffic rules and regulations is essential to deter reckless driving behaviors. Stricter penalties for traffic violations can act as a deterrent and encourage adherence to road safety norms.
Improved Road Infrastructure: The government should invest in improving road infrastructure, ensuring well-constructed roads, proper lighting, clear road markings and well-maintained signage.
Public Awareness Campaigns: Regular public awareness campaigns on road safety, particularly targeting vulnerable road users such as pedestrians and cyclists, can help disseminate crucial information and promote safer road habits.
Strict Alcohol Testing: Implementing random alcohol testing at checkpoints and during routine traffic stops can help identify and penalize drunk drivers.
Smart Use of Technology: Encouraging the use of technology to prevent accidents, such as installing speed cameras, using smart traffic signals and employing intelligent transportation systems, can help improve overall road safety.
Ambulance Service: Saving Lives in Accidents
In the unfortunate event of a road accident, timely medical assistance can be the difference between life and death. In India, where the road accident fatality rate is high, a well-organized and efficient ambulance service is of paramount importance.
Dedicated Emergency Helpline: Establishing a dedicated emergency helpline that connects callers with emergency medical services can significantly reduce response times.
GPS Tracking and Routing: Equipping ambulances with GPS tracking systems allows for quicker route planning and navigation, ensuring they reach accident sites faster.
Trained Medical Staff: Ambulances should be staffed with well-trained paramedics and emergency medical technicians capable of providing immediate medical assistance at the accident scene and during transportation to hospitals.
Integration with Traffic Management: Effective coordination between emergency medical services and traffic management authorities can help clear traffic jams and create a smooth passage for ambulances, reducing travel time to hospitals.
Air Ambulance Services: In remote areas or during severe traffic congestion, air ambulance services can prove crucial in transporting critical patients to hospitals promptly.
Conclusion
Road accidents in India remain a significant concern, claiming numerous lives and causing immeasurable pain and suffering. Addressing the root causes of accidents, such as poor road infrastructure, reckless driving and lack of road safety awareness, is crucial to make Indian roads safer. Simultaneously, a well-organized ambulance service with quick response times can save precious lives in the aftermath of accidents. By implementing robust road safety measures and enhancing emergency medical services, we can strive towards reducing the tragic toll of road accidents in India and building a safer and more secure transportation ecosystem for everyone.